Copyright © 2019 JIANGYIN JUNZHUO MACHINERY MANUFACTURING CO., LTD All Rights Reserved. Site MapDesigned by iwonder.cn
 jz@junzhuojx.com
jz@junzhuojx.com
 +86-0510-86382380
+86-0510-86382380
Lab type/Small batch Oscillating Granulator
Small-scale oscillating granulator typically refer to table-top equipment used in laboratories, pilot-scale testing, or small-batch production. Its core working principle is identical to large-scale models, but it prioritize flexibility and precise control in operation.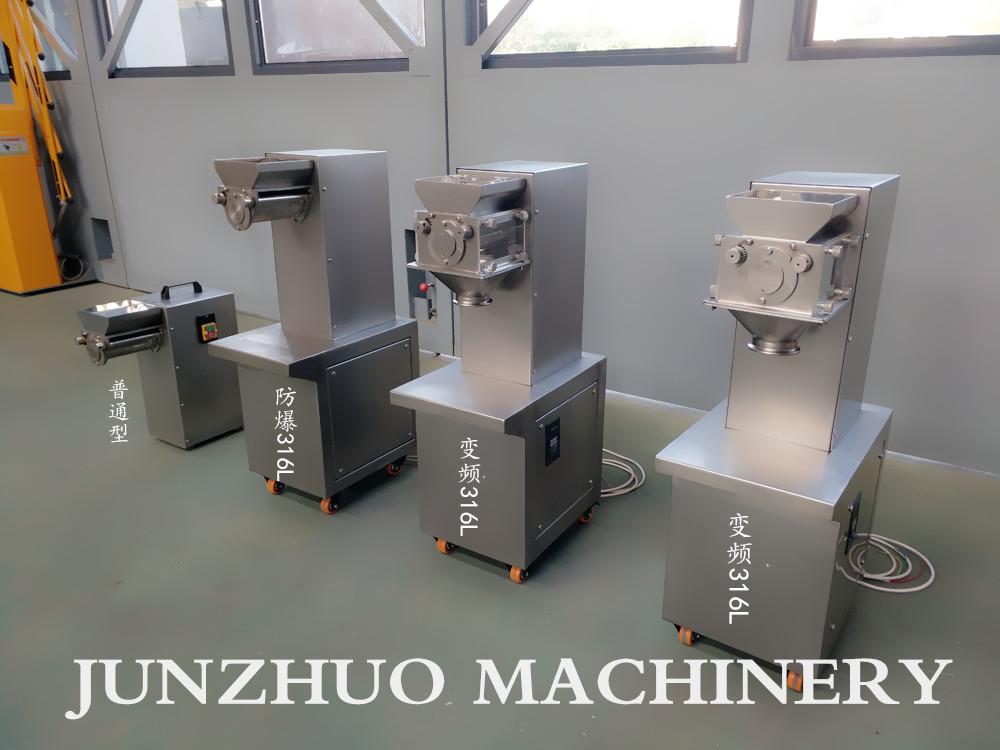
Core Characteristics of Small-Scale Oscillating Granulators
Compact Size: Featuring a table-top design, it occupies minimal space and can be easily operated on laboratory workbenches or within cleanrooms.
Small Processing Capacity: The batch processing capacity usually ranges from a few kilograms to over ten kilograms, making it ideal for research and development (R&D), formula adjustment, and small-batch production.
Flexible Operation: It allows for frequent screen sieve and material changeovers, facilitating tests of various process parameters.
Simple Structure: It typically adopts an open or semi-open design, enabling easy observation of the granulation process and convenient cleaning.
Manual Control-Focused: Most models have fixed speeds or variable-frequency speed regulation, and their operation relies more on the operator’s experience.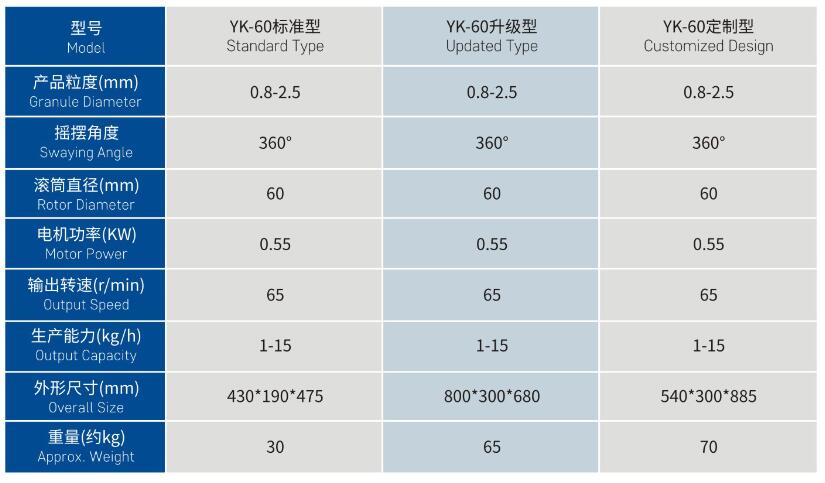
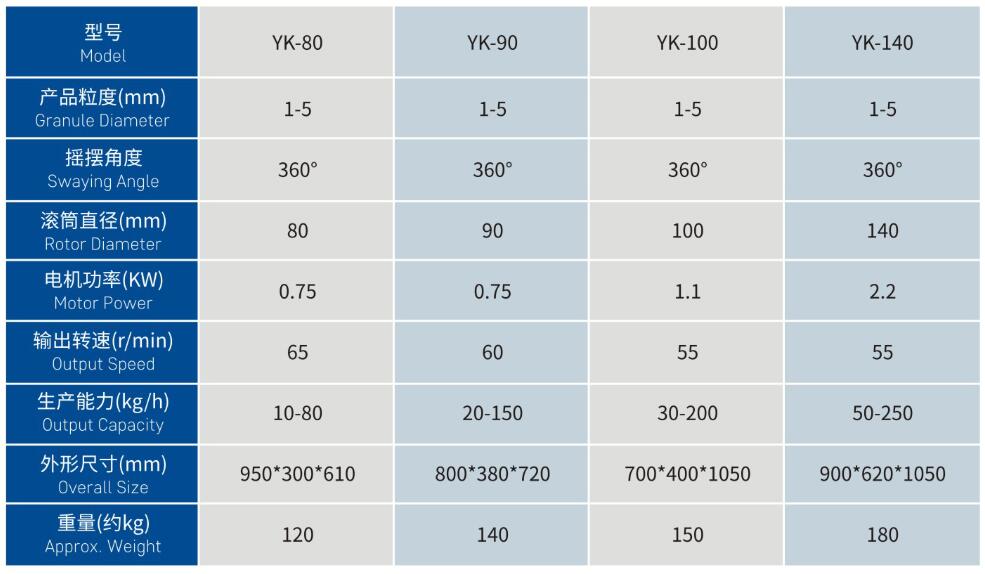
Main Application Fields
Pharmaceutical Industry: This is its core application. It processes wet soft materials (composed of medicine powders and excipients) into granules, which are then used for tableting or capsule filling.
Food Industry: It is used to produce granules for candies, seasonings, and instant drinks (such as coffee and milk powder).
Chemical Industry: It manufactures granules for catalysts, detergents, pigments, and plastics.
Research Institutes: It is applied in the process research and development of new materials and new formulas.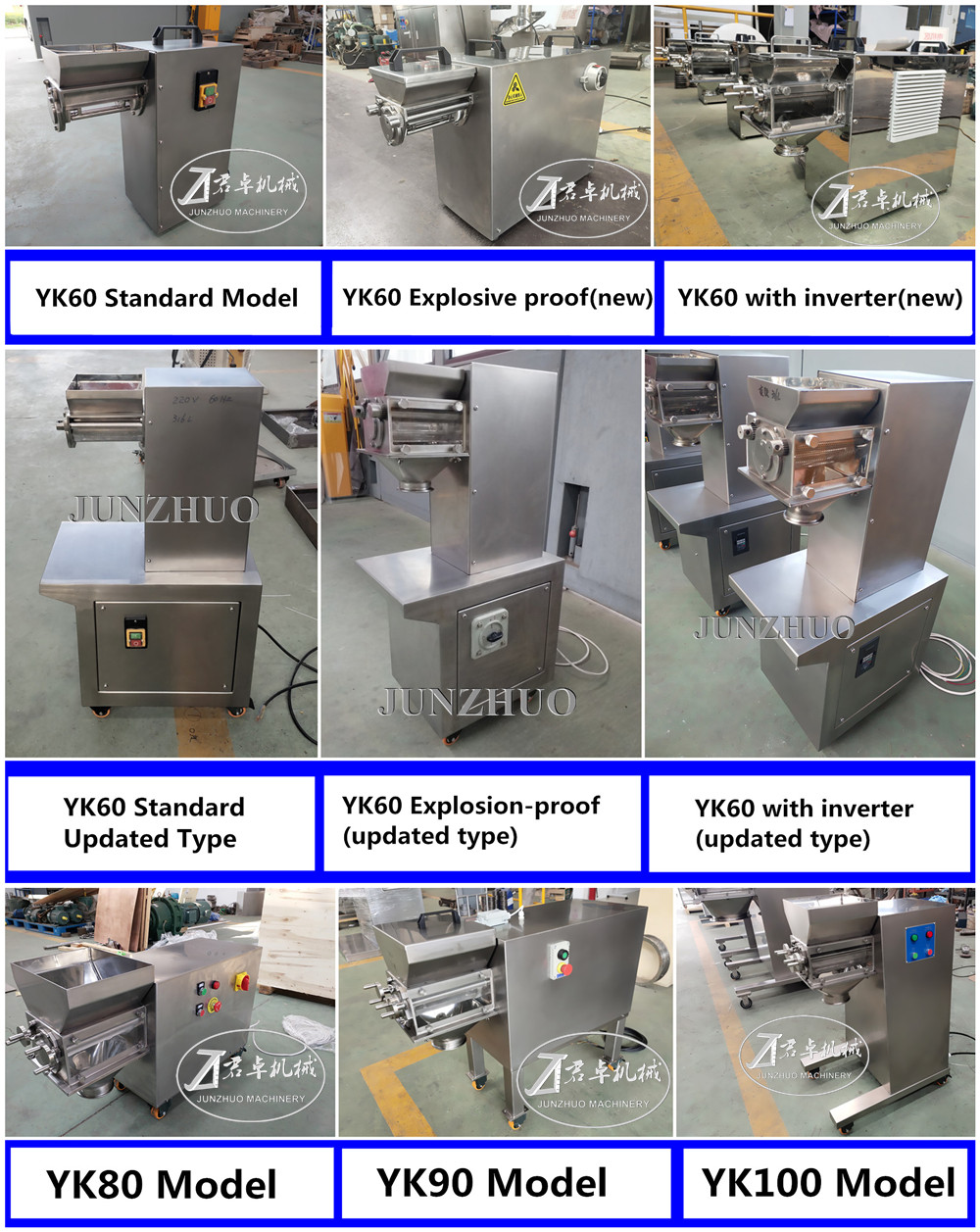
Usage Precautions
Material Humidity (Liquid Content): This is the key to successful granulation. If the material is too dry, it will be difficult to extrude into strips—resulting in low output and excessive powder. If the material is too wet, it will clog the screen sieve and form strips instead of granules. It is necessary to determine the optimal moisture content through preliminary experiments.
Screen Sieve Selection: Choose a screen sieve with an appropriate aperture based on the target particle size. Ensure the screen is securely installed to prevent loosening during the extrusion process.
Feeding Speed: Maintain uniform and continuous feeding to avoid idling of the hopper or overfilling. This ensures the uniformity of granules and stable operation of the equipment.
Cleaning and Maintenance: After working, thoroughly clean the equipment immediately, it can prevent material from drying and scaling (which may corrode the equipment or cause cross-contamination). Adding lubricating oil to the transmission components regularly.
Safe Operation: Never insert hands or tools into the hopper or extrusion area while the machine is in operation.
Video Link:
https://youtu.be/skHOV2qMZ8E?si=-4nyxpu5pQyq8gaI
https://youtu.be/FF5vPHqjbNA?si=06TWgk7bT0xaIgPO
https://youtu.be/OXjUby82Tm8?si=cxENOgaxlQNYmApT
https://youtu.be/WTnxQsImr7A?si=zEZ6HEWn2BDwSkPc
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.